Location and Geography
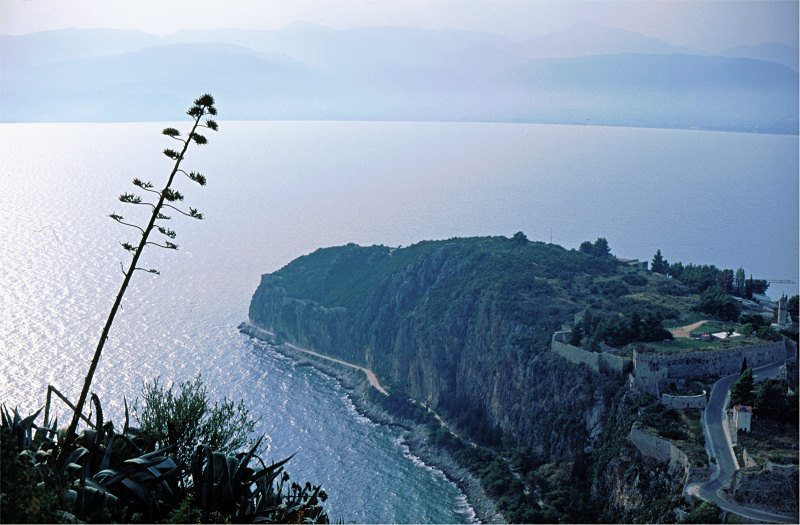
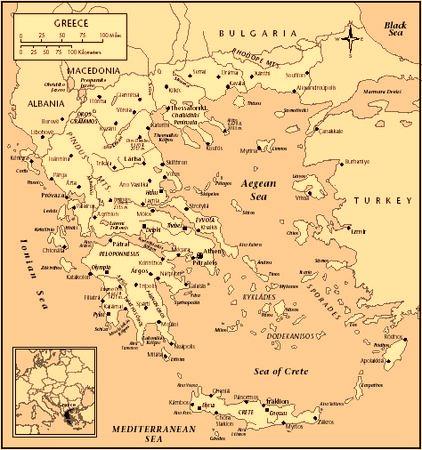
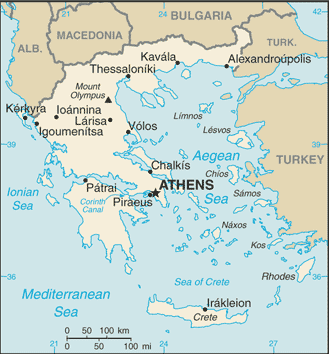
The Hellenic Republic is in southeastern Europe at the point where the Balkan peninsula extends into the Mediterranean Sea and forms a land-based connection to Anatolia and the Middle East. Initially restricted to the southern mainland and a few islands, Greece grew with the addition of the Dodecanese Islands in 1948. The country is bordered by Albania, the former Yugoslavian Republic of Macedonia, Bulgaria, Turkey, and the Aegean, Ionian, and Cretan seas.
Greece encompasses 50,935 square miles. The terrain is 80% mountainous, with its highest point, at Mount Olympus. Only 25% of the land surface is arable, and another 40% serves as pasture. There are more than 2,000 islands, 170 of which are inhabited, and a long coastline.
The climate is predominantly Mediterranean. Hot, dry summers alternate with cold, rainy winters.
There are nine recognized regions: Thrace, Macedonia, Epirus, Thessaly, Central Greece, the Peloponnesos, the Ionian Islands, the Aegean Islands, and Crete. Although these regions sometimes operated as separate entities in the past, they have been integrated into the state and their cultural distinctions are diminishing.




